Manufacturing plants often face the same daily challenges—process variations, delayed responses, manual monitoring, and unexpected losses. In many cases, machines are available, but process control is still dependent on human judgment. This is where process automation in manufacturing creates a real difference.
Instead of reacting after a problem occurs, automation helps factories control processes in real time, ensuring stability, efficiency, and predictable outcomes.
What Process Automation Really Means on the Shop Floor
Process automation in manufacturing is not just about running machines automatically. It is about controlling how a process behaves from start to finish—whether it’s temperature control, material flow, batching, or energy usage.
With industrial process automation, decisions are taken by systems based on live data, not delayed reports. This allows manufacturers to prevent issues rather than fix them later.
Use Case 1: Temperature Control in a Process Plant
Imagine a chemical or food processing unit where temperature fluctuations affect product quality. Manual adjustments often result in delays and inconsistencies.
With industrial process automation, sensors continuously measure temperature and automatically adjust control valves or heaters.
Result:
- Stable product quality
- Reduced wastage
- Zero dependency on manual intervention
This level of consistency is impossible to achieve with manual control alone.
Use Case 2: Batch Process Standardization
In batch-based manufacturing, even small variations in timing or material quantity can lead to rejected batches.
Process automation in manufacturing ensures that:
- Every batch follows the same sequence
- Exact quantities are measured automatically
- Process parameters remain within limits
Example:
A batch mixing process automatically starts, runs, and stops based on predefined logic—ensuring repeatability across every cycle.
Use Case 3: Early Detection of Process Abnormalities
Many breakdowns don’t happen suddenly—they develop over time. Manual systems often miss early warning signs.
With industrial process automation, process data is continuously analyzed to detect abnormal trends like pressure drops, vibration changes, or energy spikes.
Result:
- Maintenance teams act before failure
- Downtime is reduced
- Equipment life improves
Use Case 4: Energy & Utility Optimization
Utilities like electricity, steam, water, and compressed air are often poorly monitored.
Process automation in manufacturing tracks utility usage at the process level, helping identify inefficiencies.
Example:
If a process consumes excess energy beyond normal limits, the system flags it immediately—allowing corrective action.
Where Devanta Tech Fits into This Journey
At Devanta Tech, our role is to convert manual, experience-based processes into controlled, data-driven systems.
We follow a clear approach:
- Study the actual manufacturing process and constraints
- Design an industrial process automation that is simple and stable
- Integrate control systems, instruments, and monitoring platforms
- Enable operators with easy-to-use interfaces
- Support continuous improvement as processes evolve
Learn more about our Industrial Automation Services
Explore our IIoT & Smart Manufacturing Solutions
Benefits of Process Automation in Manufacturing
When implemented correctly, automation delivers:
- Consistent product quality
- Reduced manual dependency
- Faster response to process deviations
- Lower operating and maintenance costs
- Better control over production outcomes
More importantly, it gives manufacturers confidence in their processes.
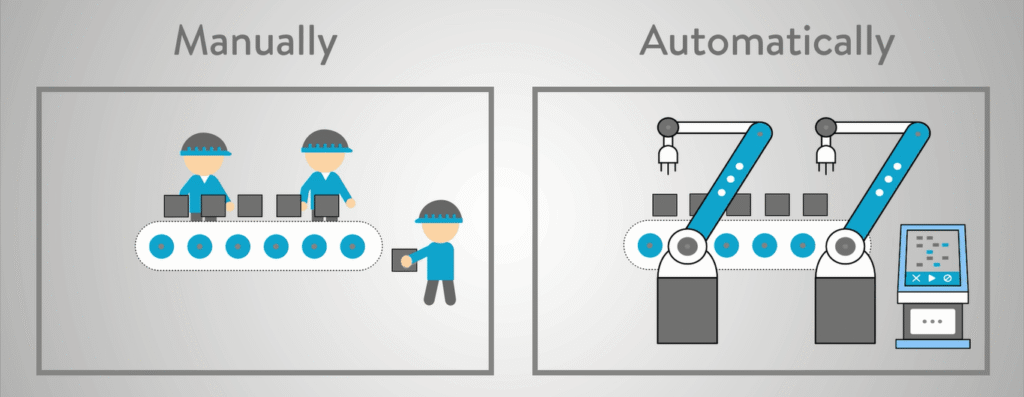
Conclusion
Process automation in manufacturing is not about complexity—it’s about control. Through structured industrial process automation, manufacturers gain visibility, stability, and efficiency across operations.
By focusing on real process behaviour rather than just machines, automation becomes a long-term growth enabler rather than a short-term upgrade.
Frequently Asked Questions [FAQ’s]
1. Can process automation be added to existing plants?
Yes. Industrial process automation can be retrofitted into existing setups with minimal disruption.
2. Which industries benefit most from process automation?
Process-heavy industries like chemicals, food & beverage, pharmaceuticals, power, and utilities benefit the most.
3. Is process automation difficult for operators to manage?
No. Modern systems are designed with simple interfaces, making operation easier than manual control.

